I recently gave a lecture at the Western Veterinary Conference called “What You Know that Ain’t Necessarily So.” The purpose of this was to take some common or controversial beliefs and practices in veterinary medicine and discuss the scientific evidence pertaining to these. This was not intended as a definitive, “final word” on these subjects, but as an illustration of how weak and problematic the evidence often is even behind widely held beliefs. In some cases, these practices or ideas may actually be valid, but without good quality scientific evidence, we should always be cautious and skeptical about them.
Eventually, I will post recordings of the presentations themselves, but for now I am posting a summary of each topic.
Each starts with a focused clinical question using the PICO format.
P– Patient, Problem Define clearly the patient in terms of signalment, health status, and other factors relevant to the treatment, diagnostic test, or other intervention you are considering. Also clearly and narrowly define the problem and any relevant comorbidities. This is a routine part of good clinical practice and so does not represent “extra work” when employed as part of the EBVM process.
I– Intervention Be specific about what you are considering doing, what test, drug, procedure, or other intervention you need information about.
C– Comparator What might you do instead of the intervention you are considering? Nothing is done in isolation, and the value of most of our interventions can only be measured relative to the alternatives. Always remember that educating the client, rather than selling a product or procedure, should often be considered as an alternative to any intervention you are contemplating.
O– Outcome What is the goal of doing something? What, in particular, does the client wish to accomplish. Being clear and explicit, with yourself and the client, about what you are trying to achieve (cure, extended life, improved performance, decreased discomfort, etc.) is essentially in evidence-based practice.
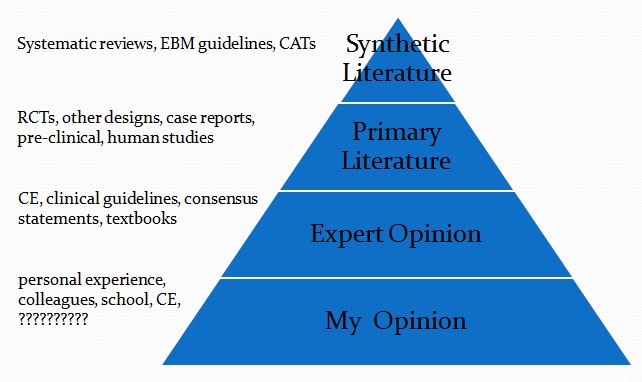
This is then followed by a summary of the evidence available at each of the levels in the following pyramid (which is a pragmatic reinterpretation of the classical pyramid of evidence that is a bit more useful for general practice veterinarians).
Finally, I list the Bottom Line, which is my interpretation of the evidence.
Immune-mediated Blood Disease & Vaccination
- Clinical question
P- healthy dogs & cats
I- routine vaccinations
C- no vaccination (fewer)
O- incidence of Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (IMHA) and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (ITP)
- Synthetic Veterinary Literature
a. No systematic reviews:
b. No CATs - Primary Veterinary Literature
- Case/control study
- Cases more likely to be vaccinated in previous month (26%) than controls (7%)
- Did not r/o pre-existing disease
Duval, D. (1996)
- 10% of cases vaccinated within 1 month
- No difference between cases and controls in time from vaccination to presentation
Carr, A.P. (2002)
- Proportion of dogs vaccinated within 2 months of onset not different between cases and controls
- Cases- 16.1%
- Controls- 44.4%
Davidow, E.B. (2004)
- Proportion of dogs vaccinated within 42 days of onset not different between cases and controls-
- Cases- 8%
- Controls- 14%
Huang, A.A. (2012)
- 4% vaccinated within 2 weeks
- Not primary purpose of study
Reimer, M.E. (1999)
- 2.4% vaccinated within 2 weeks
- Not primary purpose of study
Klag, A.R. (1993)
3. Human Literature
a. Systematic Reviews
- Database of 4.2 million children
- 55 cases of IMHA reported 1991-2001
- No association with vaccination
Naleway, A.L. (2009)
- ITP only associated with MMR
- 1-3 children per 100,000 doses
- This is lower than the rate of ITP caused by the diseases MMR prevents! (1:3000 to 1:6000 cases)
Cecinati, V. (2013)
Bottom Line
- Little evidence vaccination causes IMHA/ITP
- No consistent temporal association
- Data are weak
- Overwhelming majority of vaccinated animals do not develop these diseases
- Infection can be a greater risk for IMHA/ITP than vaccination
- Don’t vaccinate more than necessary
- Don’t vaccinate less than necessary
- Don’t avoid vaccination out of fear of IMHA/ITP
Reference
Carr AP, et al. Prognostic factors for mortality and thromboembolism in canine immune-mediated hemolytic anemia: A retrospective study of 72 dogs. J Vet Internal Med.2002;16:504-509.
Cecinati V. Hum Vaccin Immunother. Vaccine administration and the development of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in children. 2013 May;9(5):1158-62.
Davidow EB, et al. Risk factors for development of IMHA-A prospective case-control study. Abstract. VECCS 2004.
Duval D et al. Vaccine-associated immune-mediated hemolytic anemia in the dog. J Vet Internal Med. 1996;10:290-295.
Huang AA, et al. Idiopathic immune-mediated thrombocytopenia and recent vaccinations in dogs. JVIM 2012; 26: 142-148.
Klag AR, et al. Idiopathic immune-mediated hemolytic anemia in dogs: 42 cases (1986-1990). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1993;202:783-788.
Naleway AL. et al. Risk of immune hemolytic anemia in children following immunization. Vaccine. 2009 Dec 9;27(52):7394-7.
Reimer ME, Troy GC, Warnick LD. Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia: 70 cases (1988-1996). J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 1999;35:384-391










Nice timing ! I was just looking to respond to a Facebook post about this.
Thanks for an excellent overview of IMHA/ITP. Our 11 1/2 year old standard poodle was diagnosed with ITP in 2009 and many of the owners of ITP dogs that we have met over the internet since that time are absolutely convinced that vaccinations caused their dog to develop this terrible disease. Our poodle was not given any vaccinations anywhere close to the time she developed ITP and her internist told us in the beginning that her case appeared to be truly idiopathic as we could not even begin to correlate any event that may have brought it on. After she came down with ITP, I also did some internet research about this disease and came to pretty much the same conclusion that you have shown here and have never seen anything since that time to make me think otherwise. It is interesting to me that the internist has mentioned several times over the years that she sees ITP diagnoses in groups; i.e, she will have none for some period of time and then she will diagnose and treat a number of dogs in a short time. Merely an observation by her with no attempt to explain why that is so. Our poodle has been very fortunate in that she relapsed twice in 2010 and 2011, and after removal of her spleen, she has been in remission. So many dogs and owners are not so lucky as ITP has such a high initial mortality rate and, from my strictly layman’s observations, it seems that early diagnosis and aggressive treatment is so important. I have no doubt that our poodle would not be here if not for the excellent efforts of her internist and also for the fact that the internist mentioned to us once that our poodle seems to tolerate low platelets well.
Skeptvet, speaking of vaccination, have you seen this Jimmy Kimmel clip yet? It’s pretty funny: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QgpfNScEd3M&feature=youtu.be
I love this “series”. Thanks!
^ … and the update too, LOL.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i2mdwmpLYLY&feature=youtu.be
Wow, those responses from viewers are shockingly vitriolic and reactionary–and yet, not shockingly, really; Skeptvet gets those sorts of comments routinely. I love that 100% of child respondents chose not to get jabbed with a needle. LOL
Pingback: Canine Nutrigenomics by Dr. Jean Dodds: Science as Windowdressing | The SkeptVet